Avda. Los Pajaritos 3195, Oficina 1410
Edificio Centro Maipú
Maipú – Santiago
Avda. Los Pajaritos 3195, Oficina 1410
Edificio Centro Maipú
Maipú – Santiago





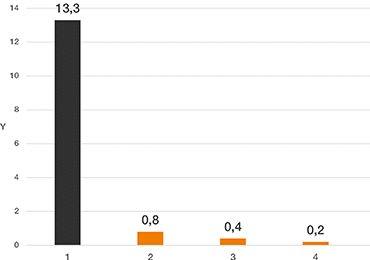


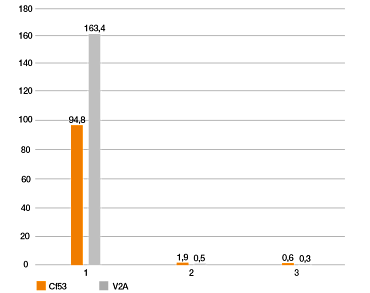

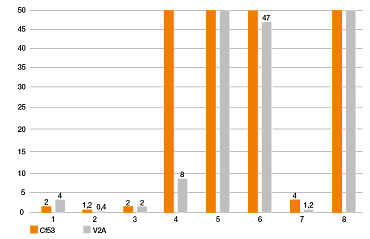

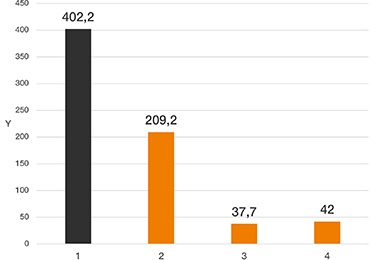
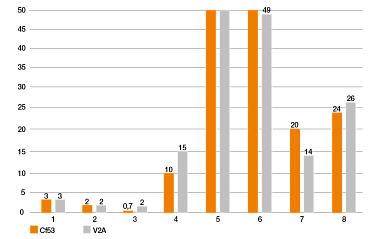
Y= índice de desgaste [µm/km]
Eje x: materiales de prueba
Resultado de la prueba:
Durante la prueba de giro, las propiedades tribológicas de los filamentos de iglidur permitieron una resistencia al desgaste hasta 50 veces superior a la de los materiales de impresión 3D convencionales, como el ABS. El polímero resistente al desgaste garantiza una vida útil mucho más larga de los cojinetes de fricción y otros componentes.
¿Cuánto durará un cojinete iglidur impreso en su aplicación? Solo tiene que introducir los requisitos y determinar la vida útil online con el calculador gratuito de la vida útil de los cojinetes de fricción.

Parámetros de la prueba:
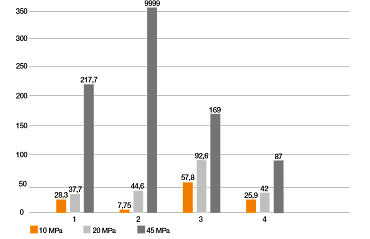
Eje y: índice de desgaste [µm/km]
Eje x: materiales de prueba
1. iglidur I3 (impresión 3D SLS)
2. iglidur I180 (impresión 3D FDM)
3. iglidur G (inyección)
4. iglidur W300 (inyección)

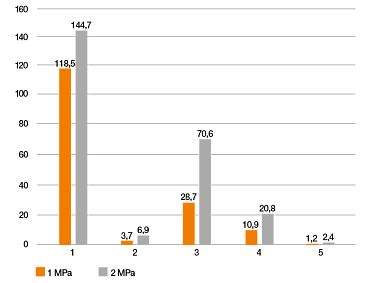

Parámetros de la prueba:
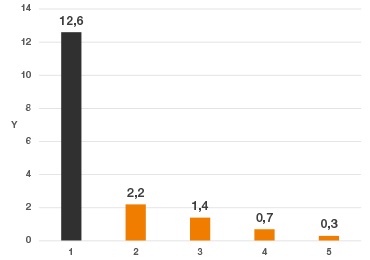




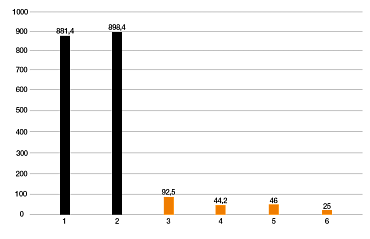

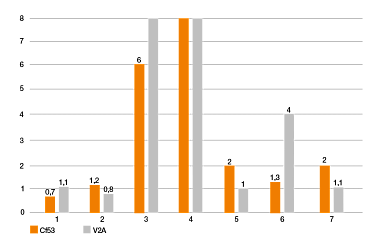
Parámetros de la prueba:
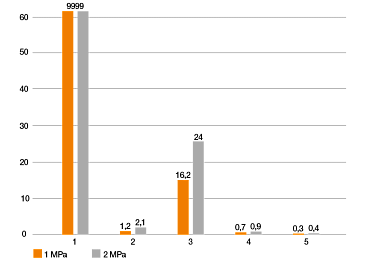

Parámetros de prueba:
pivoting oscilación 1.440°:
n = 64 r. p. m.
M = 2,25 Nm
z= 30
m= 1
b = 6 mm
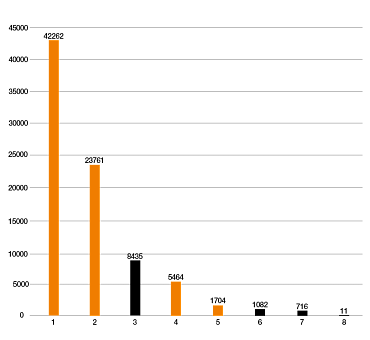
Parámetros de la prueba:

De lunes a viernes de 7:00 a 20:00Sábados de 8:00 a 12:00
24h